How Much Power Does CCTV Use and What is the Relationship Between Watt and Kwh?
- Richard Wang
- March 18, 2022
- 8:05 pm

Preface
How much power does CCTV use is an important parameter. Based on this parameter, we know the amount of electricity used by CCTV cameras every day, month, and year so as to calculate the operation cost of the video surveillance project. At the same time, for some scenarios that require UPS battery backup for CCTV cameras, we need to calculate the UPS power and battery capacity we need to configure based on CCTV camera power consumption. This article will briefly introduce how to calculate how much power does CCTV use based on the parameters in the CCTV camera manufacturer's catalog.
Reference Video:
Table of Contents
1.First Step-Find Out Rated Power of the CCTV Camera
Let’s take an Axis M4215-LV dome camera as an example to calculate.

Source: Axis M4215-LV Dome Camera
Generally, after we get a CCTV camera, we can find their product catalog on the manufacturer’s website. For example, when we open the catalog of the Axis M4215-LV Dome Camera, we can find the following parameters:
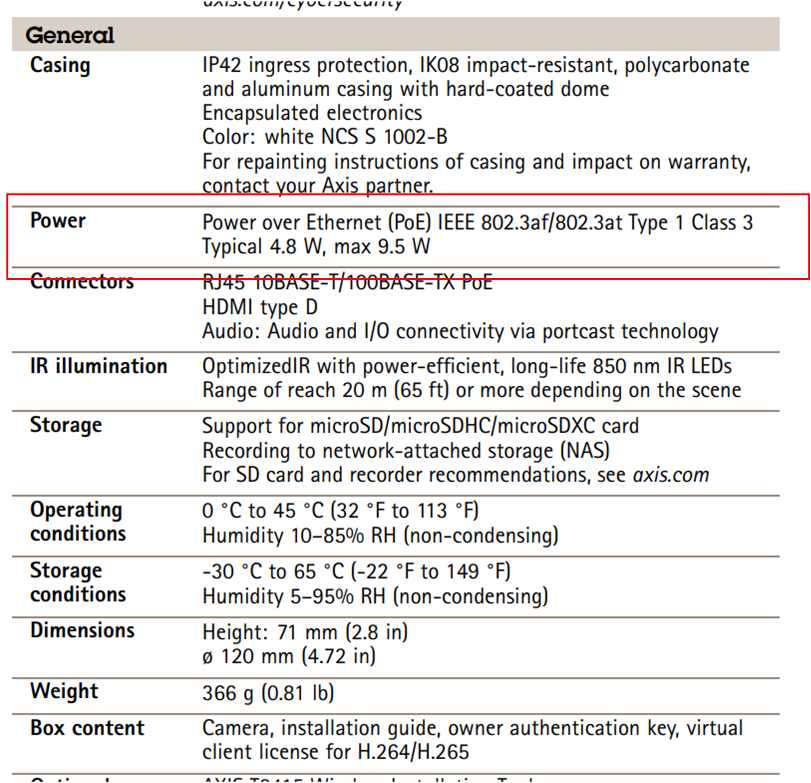
As shown in the figure above, we can see that there are two parameters related to our calculation. The first is typical 4.8W. The second is max 9.5W.
Typical 4.8W
Because the operation of CCTV camera is a dynamic process, its power consumption is also a dynamic process. The power consumption is related to various conditions such as the current function, the resolution of the video, whether IR is turned on, etc. Typical 4.8W can be understood as the average power consumption of 4.8W.
Max 9.5W
Max 9.5W can be considered as the power consumption of CCTV camera when all functions are turned on and running at the highest resolution. It can be expected that the power consumption of CCTV camera during operation will not exceed this value.
These two parameters need to be used according to your scenario. If you are just calculating how much power does CCTV use to estimate the daily electricity cost (Operation Cost) of CCTV camera, then using typical 4.8W is a more reasonable choice. If you want to calculate CCTV UPS power backup and battery capacity, it is recommended to use max 9.5W and make some conversions for calculation.
This article mainly focuses on the first scenario, how to calculate the power consumption of CCTV camera. If you need to clarify UPS and battery calculation for CCTV camera, you can refer to the following articles for more information:
How to Calculate UPS and Battery for CCTV System?
2.Second Step-Understand the Relationship Between Watt and Kwh
When you ask the question “How much power does CCTV use”, what you actually want to ask is how much Kwh does CCTV use? Because Kwh is the unit we use to pay our electricity bills. So we actually need to convert the typical 4.8W parameter found in the previous chapter into Kwh so that we can understand the electricity bill we need to pay or the operating cost of CCTV cameras.
To explain this question, first we need to clarify what kWh is:
The kilowatt-hour is a composite unit of energy equal to one kilowatt (kW) sustained for (multiplied by) one hour.
Source:Kilowatt-hour
This explanation is very theoretical and difficult to understand, so let’s try to draw a picture to explain it.

First of all, we need to clarify a concept, 1kWh = 1000Wh, which will be used in subsequent calculations.
The above picture is the explanation of 1kWh,or we say is 1000Wh.First, we split the word Kilowatt-hour into two words, Kilowatt and hour. In fact, Kilowatt means that the rated power of our device is 1000w, and one hour is converted to second, which is 3600 seconds. So 1 Kilowatt-hour is actually the amount of electricity consumed by a device with a rated power of 1000W running for 3600 seconds. So it can be simply understood that 1000W is the amount of electricity consumed by this device per second, representing the instantaneous state of electricity consumed by this device at this second. And 1 Kilowatt-hour refers to the electricity consumed by this device after running for one hour, which is the cumulative total amount of one hour.
If we put aside this issue and understand it as the water flow rate and the total amount of water that finally flows out:

In fact, it is similar to the water flow rate and the total amount of water that finally flows out. If the water flow rate is 1000L/Second, this speed represents the instantaneous state of the water flow rate in one second. And this instantaneous state of the water flow rate needs to be multiplied by the time the water flows out to get the total amount of water that finally flows out. If you want to calculate how much water flows out in an hour, you need to multiply the water flow rate 1000L/Second by 3600 seconds (one hour) to get the total amount of water that finally flows out.
So if we imagine the 1000W device reated power as the water flow rate and Kwh as the total amount of water that finally flows out, isn’t it much easier to understand?
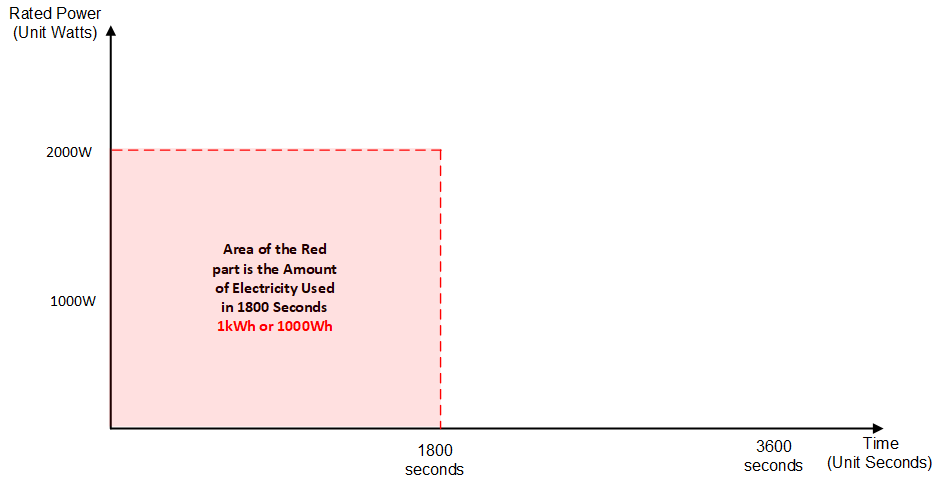
Let’s change the understanding of the above picture a little bit. We have a device with a rated power of 2000W. It runs for half an hour (1800 seconds). How many kWh does it consume? From the above picture, we can see that it is actually 1kWh. Again, 1kWh is the cumulative value of the power consumed by a device in an hour. In the example above, although the device only runs for the first half hour and does not run for the second half hour, its cumulative power consumption for one hour is still 1kWh.
3.Thrid Step-Calcuate How Much Power Does CCTV Use in kWh
We have found out in chatper 1 that the typical power of CCTV camera is 4.8W, so we can start to calculate its power consumption in kWh.
First remember that kWh refers to the cumulative value of power consumed by a device over a period of time. So we need to define time, so let’s say one day, one month (30 days), and one year (365 days), these three time periods are assumed.
CCTV camera power consumption in one day (kWh)
One Day Has How Many Seconds =60*60*24 = 86400 Seconds
CCTV Camera Power Consumption in one Day(In Watt-hour) = (4.8W*86400Seconds)/3600 Seconds Per hour = 115.2Wh
Please note that our calculations here are only Watt-hours, we need to convert to Kilowatt-hours. Remember what we said before, 1kWh = 1000Wh. So we can get the following calculation:
CCTV Camera Power Consumption in one Day(In Kilowatt-hour) = 115.2Wh/1000 = 0.1152kWh
CCTV camera power consumption in one month(30Days) (kWh)
CCTV Camera Power Consumption in one Month = CCTV Camera Power Consumption in one Day(In Kilowatt-hour) * 30 Days = 0.1152kWh*30 = 3.456kWh
CCTV camera power consumption in one year (365Days) (kWh)
CCTV Camera Power Consumption in one year= CCTV Camera Power Consumption in one Day(In Kilowatt-hour) * 365 Days = 0.1152kWh*365 = 41.472kWh
4.Actual Use
When using it, please pay attention to the rated power of your camera and find the accurate rated power value from the CCTV camera catalog. In addition, please pay attention to the Technical Tools section of the Edgeware website. We will update the relevant automatic calculation tools in the future. However, it is still recommended to understand this concept, which will help you better estimate the operating cost of the entire project in the subsequent video surveillance project.

